
Tutoring
The government’s £1bn National Tutoring Programme gives schools support from tutors and in-school academic mentors. It has appointed three delivery partners, Tribal Group, Education Development Trust and Cognition Education, to quality assure tuition partners, recruit and deploy academic mentors and train new tutors.
Academic mentors work alongside existing school staff to provide one-to-one and small group, subject-specific tuition. Last year, 1,124 mentors were placed in 946 schools across England to support 103,862 disadvantaged pupils.
Academic mentors must hold a minimum of three A-levels at A*-C grade (or equivalent) and a minimum of a grade 4 (C grade) in English and Maths at GCSE level. Previously the requirement was for applicants to have a degree at 2.2 or above or Qualified Teacher Status (QTS). Academic mentors are currently offered training through Liverpool Hope University. Education Development Trust (EDT) has been appointed as training provider for the NTP programme in 2022/23 and will be sharing further details of its training offer in due course. The role can be a step into a career in teaching – 30 per cent of academic mentors without QTS were accepted onto a teacher training programme during the last academic year.
Tutors are recruited and trained by organisations signed up as tuition partners. A school-led route is delivered by school staff, who receive online training.
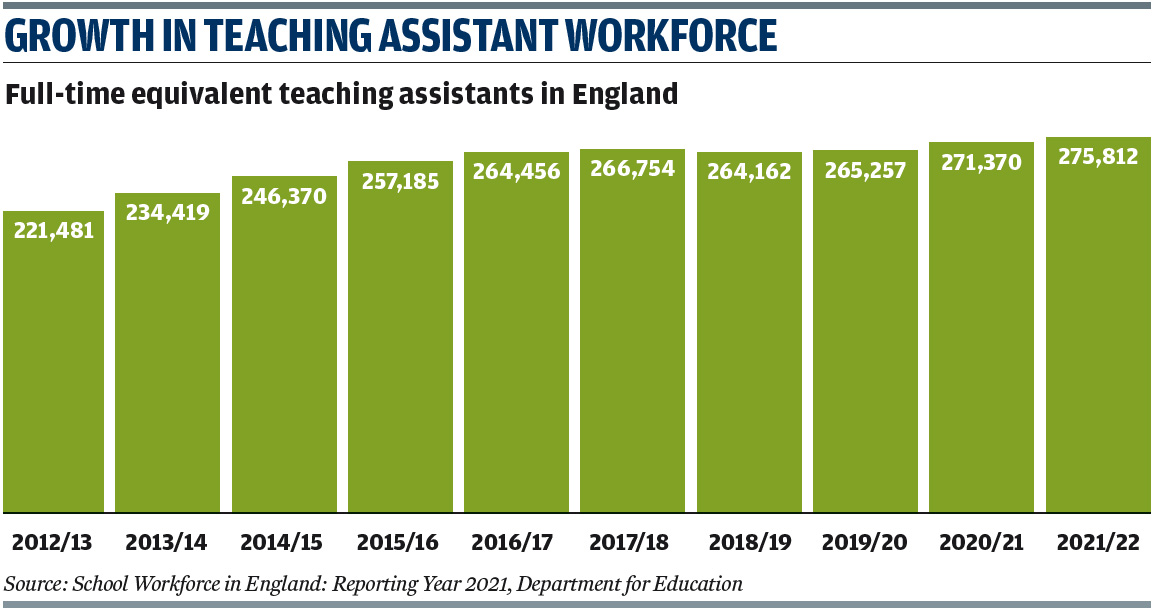
Teaching assistants
The number of full-time equivalent teaching assistants (TAs) in England has increased by 4,400 since 2020, standing at 275,812. TAs make up 28 per cent of the school workforce.
There are teaching assistant qualifications available from Level 1 to Level 4, as well as a Level 3 teaching assistant apprenticeship. Students taking the Level 3 Education and Childcare T-Level can choose to specialise in Assisting Teaching. TAs can progress into the role of higher level teaching assistant (HLTA), which involves an assessment against 33 standards. In secondary schools TAs can be known as learning support assistants (LSAs). A National Education Union survey published in April found TAs take on more work than their contract allows, with 40 per cent regularly working as cover supervisors.
From September 2022, consultancy MaximisingTAs is partnering with the National College of Education to offer the Future Leaders Programme: Maximising Impact of Support Staff, a 12-month CPD programme aimed at TAs, HLTAs and LSAs which includes a Level 3 Team Leader/Supervisor Apprenticeship.
Special educational needs and disabilities
All mainstream schools are required to have a special educational needs co-ordinator (Senco), responsible for assessing, planning and monitoring the progress of children with special educational needs and disabilities (SEND). Sencos must be qualified teachers. Newly appointed Sencos without more than a year’s past experience of the role must achieve a postgraduate National Award in Special Educational Needs Co-ordination within three years of appointment.
The government is currently consulting on proposed changes to SEND and alternative provision in England. These include a single national SEND and alternative provision system and new local SEND partnerships. The government intends to consult on the introduction of a new Senco National Professional Qualification for school Sencos and increase the number of staff with an accredited Level 3 Senco qualification in early years settings to improve SEND expertise.
A first round of 36 special schools are set to open in September 2022 followed by another round in September 2025 following a bidding process. The schools will offer specialist support and education for pupils with needs such as autism, severe learning difficulties or social emotional and mental health conditions.
Nasen provides training, support, consultancy and coaching in SEND and “inclusion by design”. Membership became free to all UK individuals in January 2021. Nasen also offers accredited courses such as a Level 3 and 4 SEND Casework Award and Youth Mental Health First Aid. The Whole School SEND Consortium brings together organisations and individuals who share a commitment to improving the educational experiences and outcomes for children and young people with SEND. Free CPD resources can be found online at Whole School SEND at www.wholeschoolsend.org.uk.
PSHE
Personal, social, health and economic (PSHE) education is compulsory in all state-maintained schools alongside relationships education in primary schools and relationships and sex education in secondary schools. The PSHE Association offers a range of continuing professional development (CPD) and one-to-one support opportunities.
Other roles
Government funding for educational psychologist training has been extended, with an expected 203 funded places available for September 2023.
Every school in England is required to have a named “careers leader”. The Careers and Enterprise Company delivers government-funded training for careers leaders, with a £1,000 bursary offered on completion which can be spent on further CPD. At the end of May 2022, 2,117 careers leaders had completed the training offer and by the end of October 2023 this will reach 3,500.
Read more in CYP Now's Children’s Workforce Guide to Qualifications and Training

